- Contact Person : Mr. Wang Barry
- Company Name : Zhejiang Orient Gene Biotech Co., Ltd.
- Tel : 86-572-5226222
- Fax : 86-572-5226222
- Address : Zhejiang,Huzhou,Jiankang Industrial Area(medicine),Anji Economic Development Zone,Zhejiang
- Country/Region : China
- Zip : 313300
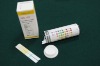
Urinalysis test Strip
URTEST 10T Reagent Strips For Urinalysis are in vitro diagnostic test devices that use reagents for qualitative and semi-quantitative urinalysis. The strips are for professional use only.
URTEST 10T Reagent Strips For Urinalysis are intended for use to detect conditions indicating possible diabetes, metabolic abnormalities, liver diseases, kidney function, and urinary tract infections. Test results can be used along with other diagnostic information to rule out certain disease states and to determine if microscopic analysis is needed.
Summary and Explanation of TestsURTEST 10T Reagent strips provide tests for Glucose, Bilirubin, Ketone (acetoacetic acid), Specific Gravity, Blood, pH, Protein, Urobilinogen, Nitrite and Leukocytes in Urine.
Test PriniciplesUrobilinogen: this test is based on the Ehrlich reaction in which p-diethylamino benzaldehyde in conjunction with a color enhancer reacts with urobilinogen in a strongly acid medium to produce a pink-red color.
Bilirubin: The direct bilirubin and dichlorobenzene diazonium produce fuchsia azo dyes in a strongly acid medium.
Ketone: The acetoacetate and sodium nitroprusside cause a reaction in the alkaline medium, which produces a violet color.
Blood: Hemoglobin acts as a peroxidase. It can cause peroxidase to release neo-ecotypes oxide [O]. [O] oxidizes the indicator and causes the color change.
Protein: The test is based on the protein-error-of-indicators principle. An ion in the specific pH indicator attracted by cation on the protein molecule makes the indicator further ionized, which changes its color.
Nitrite: Nitrite in the urine and aromatic amino sulphanilamide are diazotized to form a diazonium compound. The diazonium compound reacting with tetrahydro benzo(h) quinolin 3-phenol causes the color change.
Leukocytes: Granulocyte leukocytes in urine contain esterase that catalyze the hydrolysis of the pyrrole amino acid ester to liberate 3-hydroxy-5-pheny pyrrole. This pyrrole reacting with diazonium forms a purple color.
Glucose: The glucose oxidized by glucose oxidase catalyzes the formation of glucuronic acid and peroxide hydrogen. Peroxide hydrogen releases neo-ecotypes oxide [O] under the function of peroxidase. [O] oxidizes iodide potassium, which causes the color change.
Specific Gravity: Electrolyte (M+X-) in the form of salt in urine reacts with poly methyl vinyl ether and maleic acid (-COOH), which is a weak acid ionic exchanger. The reaction produces hydrogenous ionogen, which reacts with a pH indicator that causes the color change.
pH: Applied to acid alkali indicator method.
Test ProcedureGather Materials1. Dry and clean plastic container
2. Toilet paper
3. Watch with a second hand or stopwatch (if you read the strip visually)
4. Urinalysis reagent strips
5. Clinitek 50, 100, 200 or 500 Urine analyzer (if you read the strip instrumentally)
Perform Tests1. Immerse the reagent area of the strip in the urine specimen and take it up quickly and immediately. Start timing if reading visually.
2. Run the edge of the strip against the rim of the container to remove excess urine. Lay the strips on a paper towel with the reagent areas upward.
3. If reading visually, hold the strip up horizontally and compare the reagent areas on the strip to the corresponding color chart on the bottle label at the exact times specified and in good light. Hold the strips close to the color blocks and match carefully. Make note of the result. Color changes after 2 minutes are of no diagnostic value. If reading by instrument, carefully follow the directions given in the instrument operating instruction. The instrument will automatically read each reagent area at a specified time.
4. Dispose of strips with laboratory waste. Do not flush down toilet.
Important Notes
1. Do not take the strips from the bottle unless they are for immediate use.
2. Do not touch reagent areas of strips.
3. Do not use strips beyond the expiration date.
4. Each strip can be used only once.
5. Large amounts of ascorbic acid may effect the test for glucose, bilirubin, nitrite, and blood [2,4].
6. Deterioration may result in discoloration or darkening of the reagent areas of the strip. If this happens, or the test results are questionable or inconsistent with expected results, check and make sure the strips are within the expiration date, and also check results with the control urine.
Sensitivity and Output Values of A10 Reagent Strip For Urinalysis
Test Pad | Sensitivity | Output Value | |
Instrumental Read | Visual Read | ||
Urobilinogen (µmol/L) | 3.2-16 | 3.2-131 | 3.2-128 |
Blirubin (µmol/L) | 3.3-8.6 | Neg.-large | Neg.-large |
Ketone (acetoacetic acid) (mmol/L) | 0.5-1.0 | Neg.-7.8 | Neg.-16 |
Blood (Ery/µL) | 5-15 | Neg.- 200 | Neg.- 200 |
Protein (g/L) | 0.15- 0.3 | Neg. -3.0 | Neg. – 20.0 |
Nitrite (µmol/L) | 13-22 | Negative - Positive | Negative - Positive |
Leukocytes (Leu/μL) | 5-15 | Neg. - 500 | Neg. - 500 |
Glucose (mmol/L) | 2.8-5.5 | Neg.-55 | Neg.-110 |
Specific Gravity | —— | 1.005-1.030 | 1.000-1.030 |
pH | —— | 5.0-9.0 | 5.0-8.5 |
Urinalysis test Strip